Email Us
What You Know or Don't Know About Switchgear?
Different types of switchgear
Gas-Insulated Switchgear
A sealed enclosure filled with insulating gas allows these switchgear components to be placed close together, reducing the overall size of the switchgear. Compact and reliable gas-insulated switchgear is always a good choice.
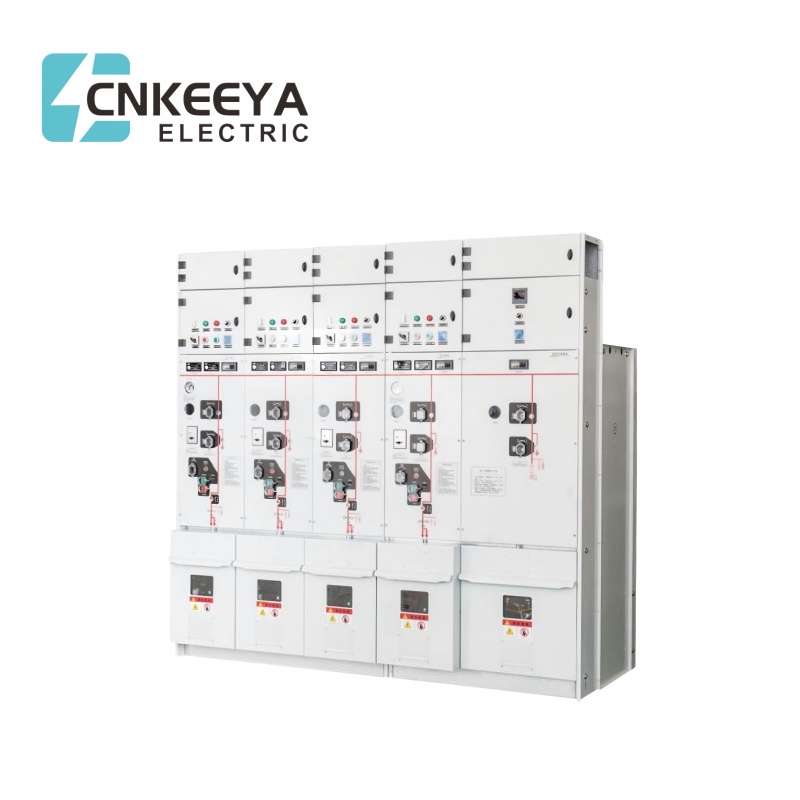
Metal-Clad Switchgear
These switchgears feature separate compartments for each internal component. While this is a larger size, it does simplify maintenance, making them a staple today.
Metal-Enclosed Switchgear
Similar to the above, the key difference between enclosed and cased switchgear is that the former does not utilize separate compartments for each component. Therefore, this switchgear is suitable for systems operating at lower voltages, such as commercial facilities.
Pad-Type Switchgear
Designed for pure practicality and primarily for use in underground distribution systems, pad-type switchgear is a unique type of switchgear. Its simple and robust design makes it durable, resistant to tampering, and easy to install externally. Pad-type switchgear also offers a wide range of insulation options, giving users more freedom of choice. Vault Switchgear
This specialized switchgear is suitable for electrical systems requiring switches to be accessible from basements or other underground areas. Its primary purpose is to provide an enclosure that can be installed at greater distances than the aforementioned options and is suitable for both dry and wet environments.
Arc-Resistant Switchgear
Designed for heavy-duty equipment, arc-resistant switchgear is fully capable of withstanding the currents and stresses generated by arc flash energy. These electrical explosions are a distinct step from conventional discharges. Arc-resistant switchgear is classified based on its resistance to arc flash energy.

How to Maintain It?
Daily Maintenance
Cleaning and Inspection
Cleaning the Equipment: Regularly remove dust, oil, and debris from the switch housing and vertical roller surfaces to ensure smooth operation.
Appearance Inspection: Observe the housing for cracks, corrosion, or deformation, and the integrity of protective coatings (such as electrostatic spray coatings).
Tightening Inspection: Check mounting screws and terminal blocks for looseness and ensure secure connections.
Operational Status Monitoring
Action Test: Manually touch the vertical roller to verify that the Level 1 Alarm (12° deflection) and Level 2 Shutdown (30° deflection) signals are output correctly. Automatic reset function: After simulating deviation, observe whether the vertical roller automatically returns to its original position to ensure the reset spring is not stuck.
Signal transmission check: Verify through the control cabinet that the alarm and shutdown signals are accurately transmitted to avoid circuit aging or poor contact.
Regular maintenance
Electrical performance testing
Insulation resistance test: Use a megohmmeter to measure the insulation resistance between the terminal block and the housing. It should be ≥500MΩ (at ambient humidity ≤85%).
Contact capacity verification: Check for oxidation or burnout of the contacts. If necessary, lightly sand the contact surface with sandpaper to ensure reliable switching at rated current (≤3A/AC380V).
Wiring check: Verify that the cables are intact and that the wire numbers are clearly marked (1 and 2 for normally open alarm, 3 and 4 for normally closed shutdown) to avoid incorrect wiring.
Mechanical component lubrication
Vertical roller bearings: Apply a small amount of high-temperature grease (such as molybdenum disulfide lithium grease) to the rotating parts to reduce wear and noise. Return spring: Check the spring's elasticity. If deformed or broken, replace it promptly to ensure a return force ≥ 50N.
Environmental adaptability check
Protection level verification: Verify the enclosure's sealing (IP67 standard) to prevent dust and water from entering.
Corrosion resistance check: Check the integrity of the zinc plating and bright chrome plating, especially for use in humid or corrosive environments.
Long-term maintenance
Rust prevention: If the equipment is idle for an extended period, apply anti-rust oil to metal parts and cover them with dust covers.
Storage: Store in a dry, ventilated room, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures (-40°C to 60°C).
Regular power-on: Test the equipment every three months to prevent internal components from moisture damage.
Troubleshooting
Abnormal signal
Cause: Loose wiring, oxidized contacts, stuck vertical rollers.
Handling: Retighten wiring, clean contacts, and adjust vertical roller verticality.
Automatic reset failure
Cause: Broken return spring, deformed vertical rollers. Solution: Replace the spring or vertical roller, ensuring the return angle is ≤30°.
Whether from the perspective of selection, installation, or maintenance, from gas-insulated switchgear to arc-resistant switchgear, each type has its unique advantages and applicable scenarios. Therefore, understanding the different types of switchgear, their respective characteristics, and their application environments is crucial. To effectively ensure the safe and stable operation of the power system, careful selection of the appropriate switchgear is essential.
- What Exactly Separates a Fuse from a Circuit Breaker
- Is Your Home’s Safety Hanging by a Single Electrical Insulator
- What Are the Common Problems in LV Switchgear and How to Troubleshoot Them
- What is the difference between a box-type substation and a traditional substation?
- In depth explanation of 10kV distribution ring main unit
- How Does A High Voltage Fuse Protect Your Critical Transformer And Capacitor Investments
Contact Us
No. 68, Wei No.19 Road, Yueqing Economic Development Zone, Yueqing City, Wenzhou City, Zhejiang Province,China
Copyright © 2025 Zhejiang Hanya Electric Appliance Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved.